Chapter 1: The Fundamental Building Blocks of Life - Cells

5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 3007 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 312 pages |
Cells are the basic units of life, the microscopic building blocks from which all living organisms are constructed. They are responsible for carrying out all of the essential functions necessary for life, including metabolism, growth, reproduction, and response to stimuli.
There are two main types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are simpler and smaller than eukaryotic cells, and they lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Bacteria are examples of prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, are more complex and contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Animal, plant, and fungal cells are all examples of eukaryotic cells.
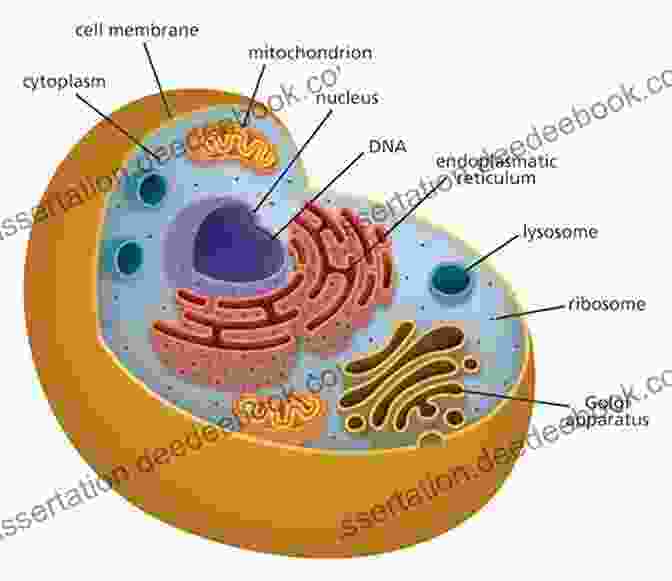
All cells share some basic features, including a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA. The cell membrane is a thin layer that surrounds the cell and protects its contents. The cytoplasm is a gel-like substance that fills the cell and contains all of the cell's organelles. DNA is the genetic material that carries the instructions for the cell's development and function.
Cell Division
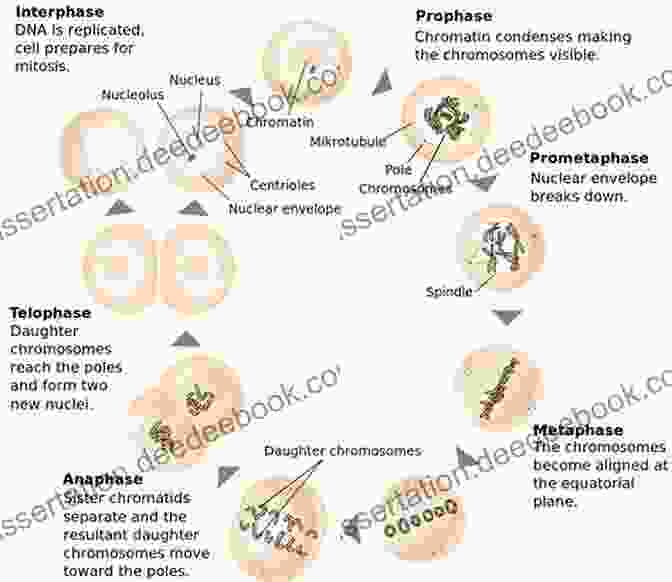
Cells divide in order to grow and repair themselves. There are two main types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis is a process that produces two identical daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. Meiosis is a process that produces four haploid cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
Mitosis occurs in the somatic cells of the body, while meiosis occurs in the germ cells of the body. Somatic cells are all of the cells in the body except for the germ cells. Germ cells are the cells that produce gametes, or reproductive cells.
Cell division is an essential process for the growth and repair of organisms. It allows organisms to grow and replace damaged or lost cells.
Cell Differentiation
As an organism develops, its cells undergo differentiation. Cell differentiation is the process by which cells become specialized in structure and function. For example, muscle cells are specialized for contraction, nerve cells are specialized for transmitting electrical signals, and skin cells are specialized for protecting the body from the environment.
Cell differentiation is controlled by a variety of factors, including gene expression and cell-cell interactions. Gene expression is the process by which the information in genes is used to make proteins. Proteins are the building blocks of cells and they play a vital role in determining the structure and function of cells.
Cell-cell interactions also play a role in cell differentiation. Cells communicate with each other through a variety of chemical signals. These signals can trigger changes in gene expression and can lead to cells differentiating into different types of cells.
Cell differentiation is essential for the development of complex organisms. It allows organisms to develop the specialized tissues and organs that they need to survive.
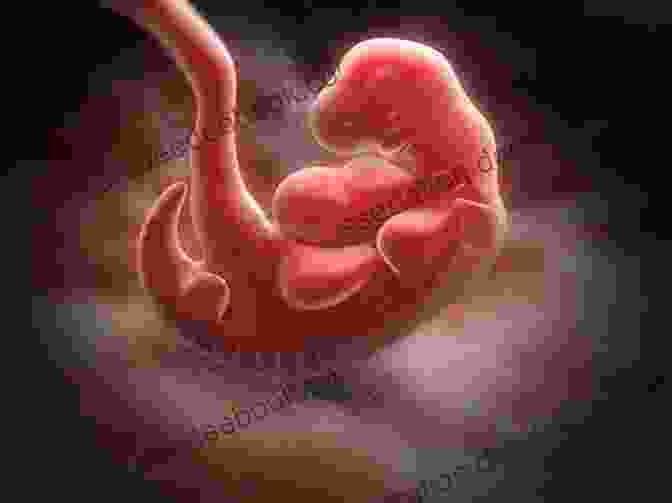
Development is the process by which an organism grows and changes from a single cell to a complex organism. It involves a series of carefully orchestrated events that must occur in the correct order for the organism to develop properly.
The first step in development is fertilization. Fertilization is the process by which a sperm and an egg fuse together to form a zygote. The zygote is the first cell of a new organism.
The zygote then undergoes a series of cell divisions, forming a ball of cells called a blastocyst. The blastocyst implants in the lining of the uterus, and the cells begin to differentiate into the different tissues and organs of the embryo.
The embryo develops rapidly during the first few weeks of pregnancy. The heart begins to beat, the limbs begin to form, and the brain begins to develop. By the end of the first trimester, the embryo is fully formed and is called a fetus.
The fetus continues to grow and develop throughout the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. By the end of the third trimester, the fetus is ready to be born.
Birth is a stressful event for both the mother and the baby. However, with proper care, most babies are born healthy and ready to begin their lives.
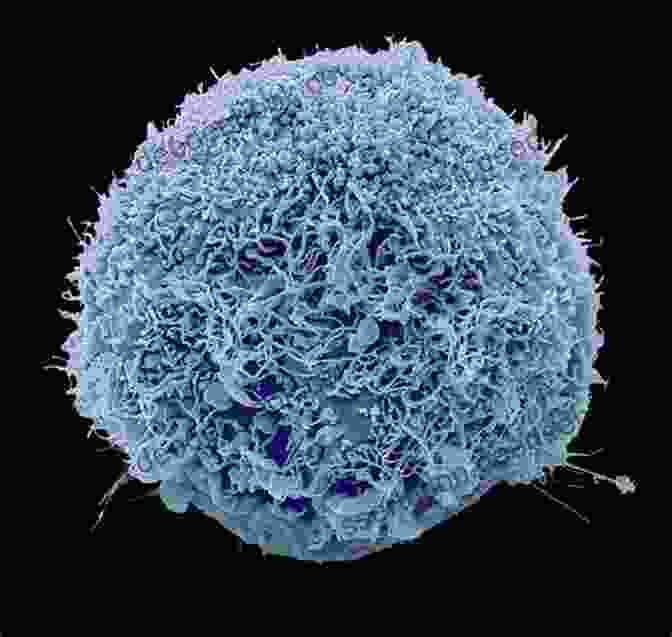
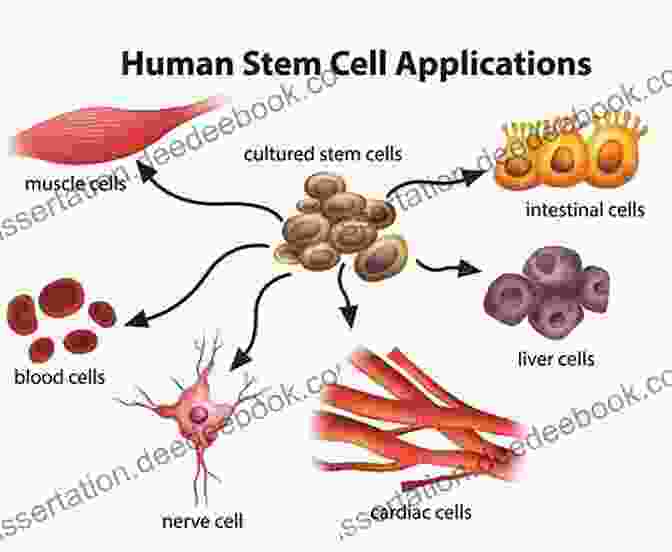
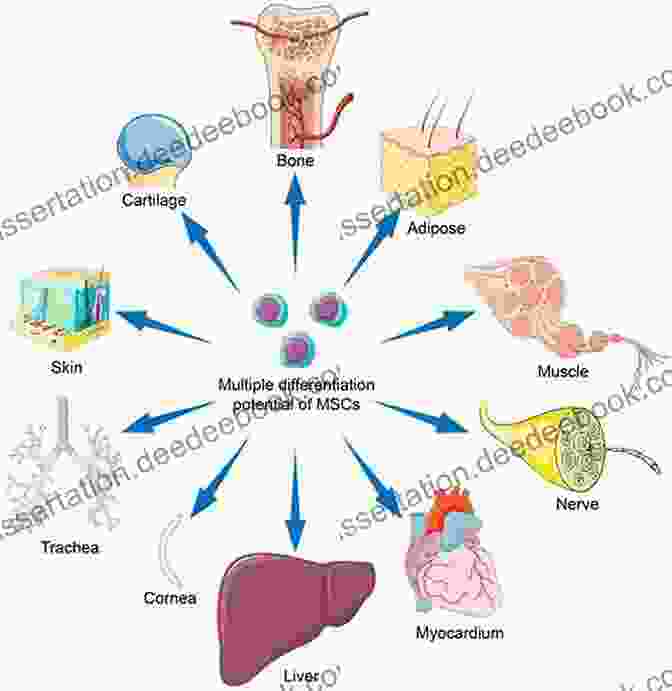
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that have the ability to differentiate into a variety of specialized cells. This makes them a valuable tool for regenerative medicine, which is the use of stem cells to repair or replace damaged tissues and organs.
Stem cells are found in the embryo, the umbilical cord, and the placenta. They can also be derived from adult tissues, such as bone marrow and fat.
Stem cells are being studied for use in treating a wide range of diseases, including heart disease, stroke, spinal cord injury, and cancer. However, there are still many challenges that need to be overcome before stem cells can be used routinely in clinical practice.
Cellular and developmental biology is a rapidly growing field of research. Scientists are gaining a better understanding of the processes that control cell division, cell differentiation, and development. This knowledge is leading to new treatments for diseases and new ways to improve human health.
The future of cellular and developmental biology is bright. This field of research has the potential to revolutionize the way we treat diseases and improve human health.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 3007 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 312 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Scroll
Scroll Classics
Classics Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Dictionary
Dictionary Thesaurus
Thesaurus Narrator
Narrator Card Catalog
Card Catalog Stacks
Stacks Archives
Archives Periodicals
Periodicals Research
Research Lending
Lending Reading Room
Reading Room Rare Books
Rare Books Literacy
Literacy Dissertation
Dissertation Storytelling
Storytelling Awards
Awards Book Club
Book Club Theory
Theory Bob Vanderberg
Bob Vanderberg Lori Demonia
Lori Demonia Sheri Reynolds
Sheri Reynolds Angel Giggly
Angel Giggly Sidney Hook
Sidney Hook Geraldine Evans
Geraldine Evans Megan Brooks
Megan Brooks 2015th Edition Kindle Edition
2015th Edition Kindle Edition John Masefield
John Masefield W E Lyons
W E Lyons Novella Bardelli
Novella Bardelli Paul L Maier
Paul L Maier Phiona Stanley
Phiona Stanley Michelle D Arcy Jewell
Michelle D Arcy Jewell Sheila West
Sheila West Christina Fanelli
Christina Fanelli Jessamyn Salinas
Jessamyn Salinas John M Alexander
John M Alexander J D Powe
J D Powe Kobo Abe
Kobo Abe
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Alexander BlairLearn The Basics Of Agile Project Management With Scrum To Skyrocket Team...
Alexander BlairLearn The Basics Of Agile Project Management With Scrum To Skyrocket Team...
 Cody RussellAbridged With An Introduction By Michael Kammen Bedford In History Culture:...
Cody RussellAbridged With An Introduction By Michael Kammen Bedford In History Culture:... Calvin FisherFollow ·14.9k
Calvin FisherFollow ·14.9k Lee SimmonsFollow ·10.1k
Lee SimmonsFollow ·10.1k Jerry WardFollow ·16.8k
Jerry WardFollow ·16.8k Chase MorrisFollow ·17.3k
Chase MorrisFollow ·17.3k Gabriel BlairFollow ·19.6k
Gabriel BlairFollow ·19.6k Kevin TurnerFollow ·9.4k
Kevin TurnerFollow ·9.4k H.G. WellsFollow ·16.2k
H.G. WellsFollow ·16.2k Daniel KnightFollow ·16.4k
Daniel KnightFollow ·16.4k

 Keith Cox
Keith CoxFrench Pieces for Flute and Piano: A Journey into...
The world of...

 Justin Bell
Justin BellThe Big Clarinet Songbook: A Musical Treasure for...
The clarinet, with its rich...

 Jamie Blair
Jamie BlairThe Metamorphoses of Ovid: A Masterpiece of...
An Epic Tapestry of Mythology and...

 Alan Turner
Alan TurnerBaa Baa Black Sheep: A Classic Sing-Along Song for Kids
Baa Baa Black Sheep...

 Bradley Dixon
Bradley DixonUnveiling the Enigmatic Shakespeare Spy: The...
Prologue: The Shadowy World...

 Gilbert Cox
Gilbert CoxUnleash Your Creativity with Plastic Craft Lace Projects:...
Plastic craft lace is a...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 3007 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 312 pages |